728x90
이전글에서 논블로킹 채팅 서버 및 클라이언트를 간단하게 만들어봤습니다. 글이 너무 길어져서 따로 코드만 첨부합니다. 코드 설명은 아래 링크를 참조하시면 됩니다.
2020/02/04 - [JAVA/기본 문법] - 네트워크_소켓(Socket) 통신_NIO 입출력(논블로킹) [2/3]
로직을 쉽게 보기 위해 객체화를 최대한 지양했습니다.
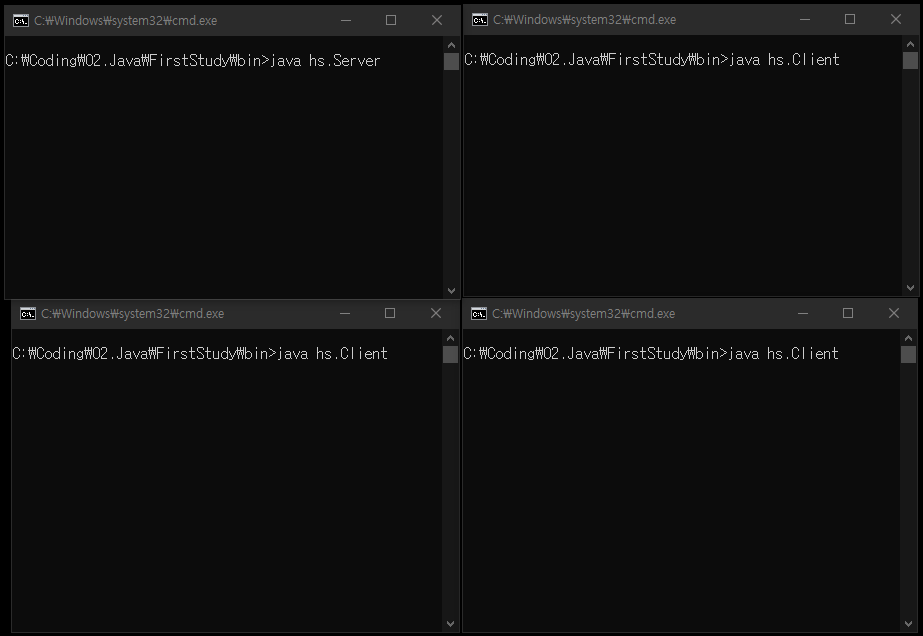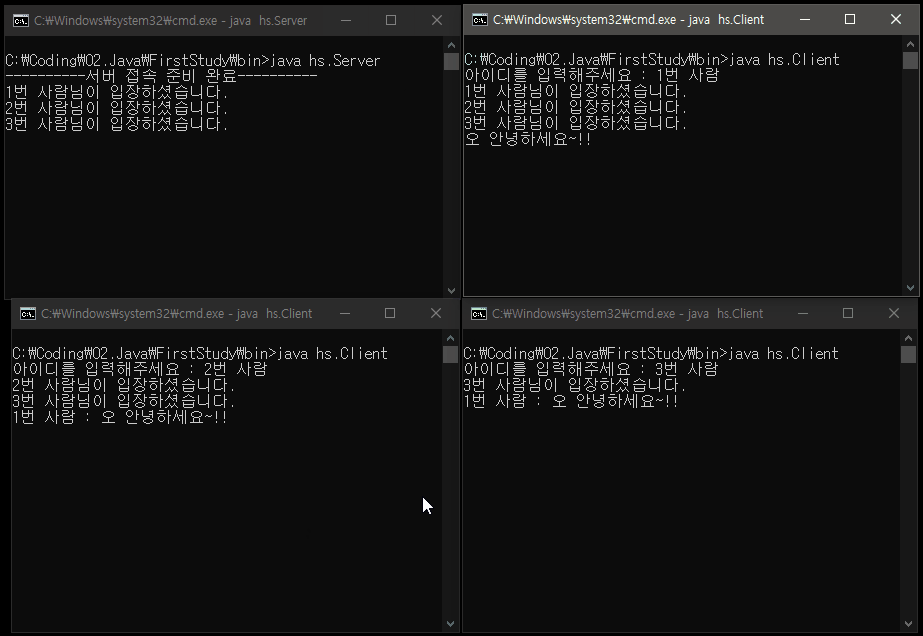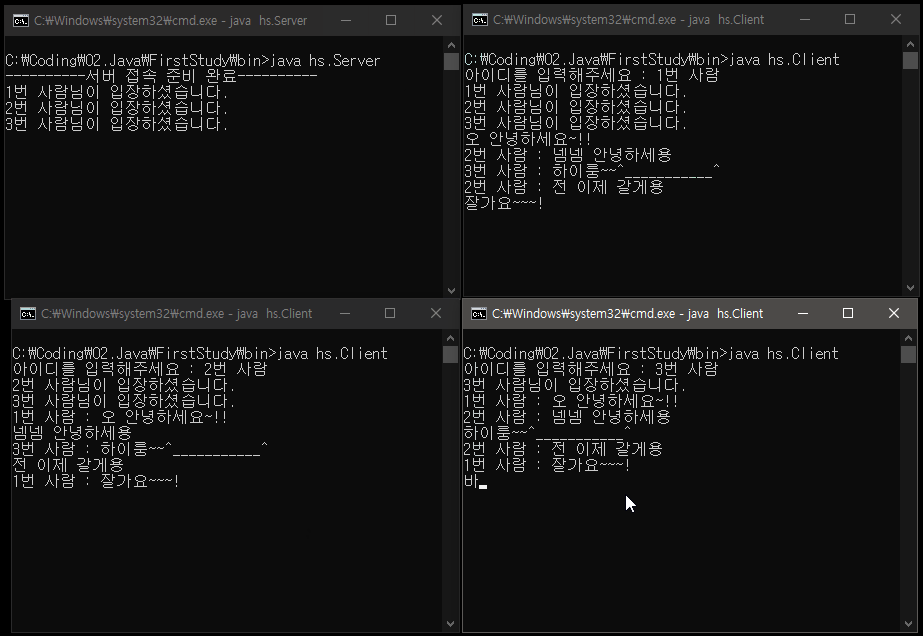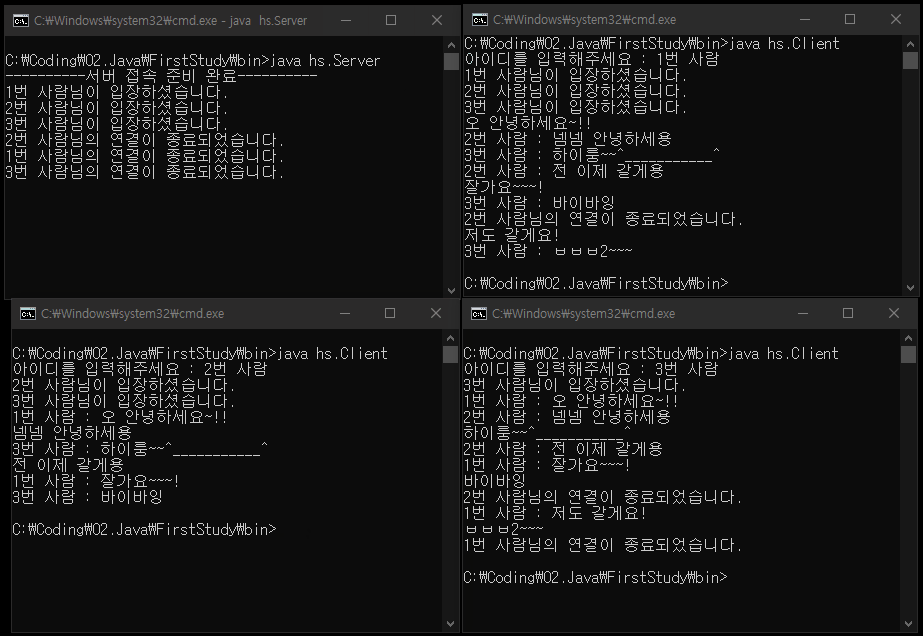
[ 스레드를 사용하지 않는 논블로킹(non-blocking) 서버 코드 ]
package hs;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.Channels;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.WritableByteChannel;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 연결된 클라이언트를 관리할 컬렉션
Set<SocketChannel> allClient = new HashSet<>();
try (ServerSocketChannel serverSocket = ServerSocketChannel.open()) {
// 서비스 포트 설정 및 논블로킹 모드로 설정
serverSocket.bind(new InetSocketAddress(15000));
serverSocket.configureBlocking(false);
// 채널 관리자(Selector) 생성 및 채널 등록
Selector selector = Selector.open();
serverSocket.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
System.out.println("----------서버 접속 준비 완료----------");
// 버퍼의 모니터 출력을 위한 출력 채널 생성
// 입출력 시 사용할 바이트버퍼 생성
ByteBuffer inputBuf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
ByteBuffer outputBuf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
// 클라이언트 접속 시작
while (true) {
selector.select(); // 이벤트 발생할 때까지 스레드 블로킹
// 발생한 이벤트를 모두 Iterator에 담아줌
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
// 발생한 이벤트들을 담은 Iterator의 이벤트를 하나씩 순서대로 처리함
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
// 현재 순서의 처리할 이벤트를 임시 저장하고 Iterator에서 지워줌
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
iterator.remove();
// 연결 요청중인 클라이언트를 처리할 조건문 작성
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
// 연결 요청중인 이벤트이므로 해당 요청에 대한 소켓 채널을 생성해줌
ServerSocketChannel server = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel clientSocket = server.accept();
// Selector의 관리를 받기 위해서 논블로킹 채널로 바꿔줌
clientSocket.configureBlocking(false);
// 연결된 클라이언트를 컬렉션에 추가
allClient.add(clientSocket);
// 아이디를 입력받기 위한 출력을 해당 채널에 해줌
clientSocket.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("아이디를 입력해주세요 : ".getBytes()));
// 아이디를 입력받을 차례이므로 읽기모드로 셀렉터에 등록해줌
clientSocket.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ, new ClientInfo());
// 읽기 이벤트(클라이언트 -> 서버)가 발생한 경우
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
// 현재 채널 정보를 가져옴 (attach된 사용자 정보도 가져옴)
SocketChannel readSocket = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ClientInfo info = (ClientInfo) key.attachment();
// 채널에서 데이터를 읽어옴
try {
readSocket.read(inputBuf);
// 만약 클라이언트가 연결을 끊었다면 예외가 발생하므로 처리
} catch (Exception e) {
key.cancel(); // 현재 SelectionKey를 셀렉터 관리대상에서 삭제
allClient.remove(readSocket); // Set에서도 삭제
// 서버에 종료 메세지 출력
String end = info.getID() + "님의 연결이 종료되었습니다.\n";
System.out.print(end);
// 자신을 제외한 클라이언트에게 종료 메세지 출력
outputBuf.put(end.getBytes());
for(SocketChannel s : allClient) {
if(!readSocket.equals(s)) {
outputBuf.flip();
s.write(outputBuf);
}
}
outputBuf.clear();
continue;
}
// 현재 아이디가 없을 경우 아이디 등록
if (info.isID()) {
// 현재 inputBuf의 내용 중 개행문자를 제외하고 가져와서 ID로 넣어줌
inputBuf.limit(inputBuf.position() - 2);
inputBuf.position(0);
byte[] b = new byte[inputBuf.limit()];
inputBuf.get(b);
info.setID(new String(b));
// 서버에 출력
String enter = info.getID() + "님이 입장하셨습니다.\n";
System.out.print(enter);
outputBuf.put(enter.getBytes());
// 모든 클라이언트에게 메세지 출력
for(SocketChannel s : allClient) {
outputBuf.flip();
s.write(outputBuf);
}
inputBuf.clear();
outputBuf.clear();
continue;
}
// 읽어온 데이터와 아이디 정보를 결합해 출력한 버퍼 생성
inputBuf.flip();
outputBuf.put((info.getID() + " : ").getBytes());
outputBuf.put(inputBuf);
outputBuf.flip();
for(SocketChannel s : allClient) {
if (!readSocket.equals(s)) {
s.write(outputBuf);
outputBuf.flip();
}
}
inputBuf.clear();
outputBuf.clear();
}
}
}
} catch (
IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
// 접속한 사용자의 ID를 가진 클래스
class ClientInfo {
// 아직 아이디 입력이 안된 경우 true
private boolean idCheck = true;
private String id;
// ID가 들어있는지 확인
boolean isID() {
return idCheck;
}
// ID를 입력받으면 false로 변경
private void setCheck() {
idCheck = false;
}
// ID 정보 반환
String getID() {
return id;
}
// ID 입력
void setID(String id) {
this.id = id;
setCheck();
}
}
[ 두 개의 스레드를 사용하는 채팅 클라이언트 코드 ]
package hs;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.Channels;
import java.nio.channels.ReadableByteChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.WritableByteChannel;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread systemIn;
// 서버 IP와 포트로 연결되는 소켓채널 생성
try (SocketChannel socket = SocketChannel.open
(new InetSocketAddress("172.30.1.29", 15000))) {
// 모니터 출력에 출력할 채널 생성
WritableByteChannel out = Channels.newChannel(System.out);
// 버퍼 생성
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
// 출력을 담당할 스레드 생성 및 실행
systemIn = new Thread(new SystemIn(socket));
systemIn.start();
while (true) {
socket.read(buf); // 읽어서 버퍼에 넣고
buf.flip();
out.write(buf); // 모니터에 출력
buf.clear();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("서버와 연결이 종료되었습니다.");
}
}
}
// 입력을 담당하는 클래스
class SystemIn implements Runnable {
SocketChannel socket;
// 연결된 소켓 채널과 모니터 출력용 채널을 생성자로 받음
SystemIn(SocketChannel socket) {
this.socket = socket;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// 키보드 입력받을 채널과 저장할 버퍼 생성
ReadableByteChannel in = Channels.newChannel(System.in);
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
try {
while (true) {
in.read(buf); // 읽어올때까지 블로킹되어 대기상태
buf.flip();
socket.write(buf); // 입력한 내용을 서버로 출력
buf.clear();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("채팅 불가.");
}
}
}728x90
'▸JAVA > 기본 문법' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 메소드 내 예외처리(try-catch-finally)에서의 리턴 처리 (0) | 2020.02.23 |
|---|---|
| 콜백(Callback) 패턴을 사용한 비동기 방식의 원리와 사용법 (8) | 2020.02.07 |
| 네트워크_소켓(Socket) 통신_NIO 입출력(논블로킹) [2/3] (4) | 2020.02.04 |
| 네트워크_소켓(Socket) 통신_IO 입출력 [1/3] (2) | 2020.02.04 |
| Thread (스레드)_스레드풀 [3/3] (2) | 2020.02.01 |

댓글